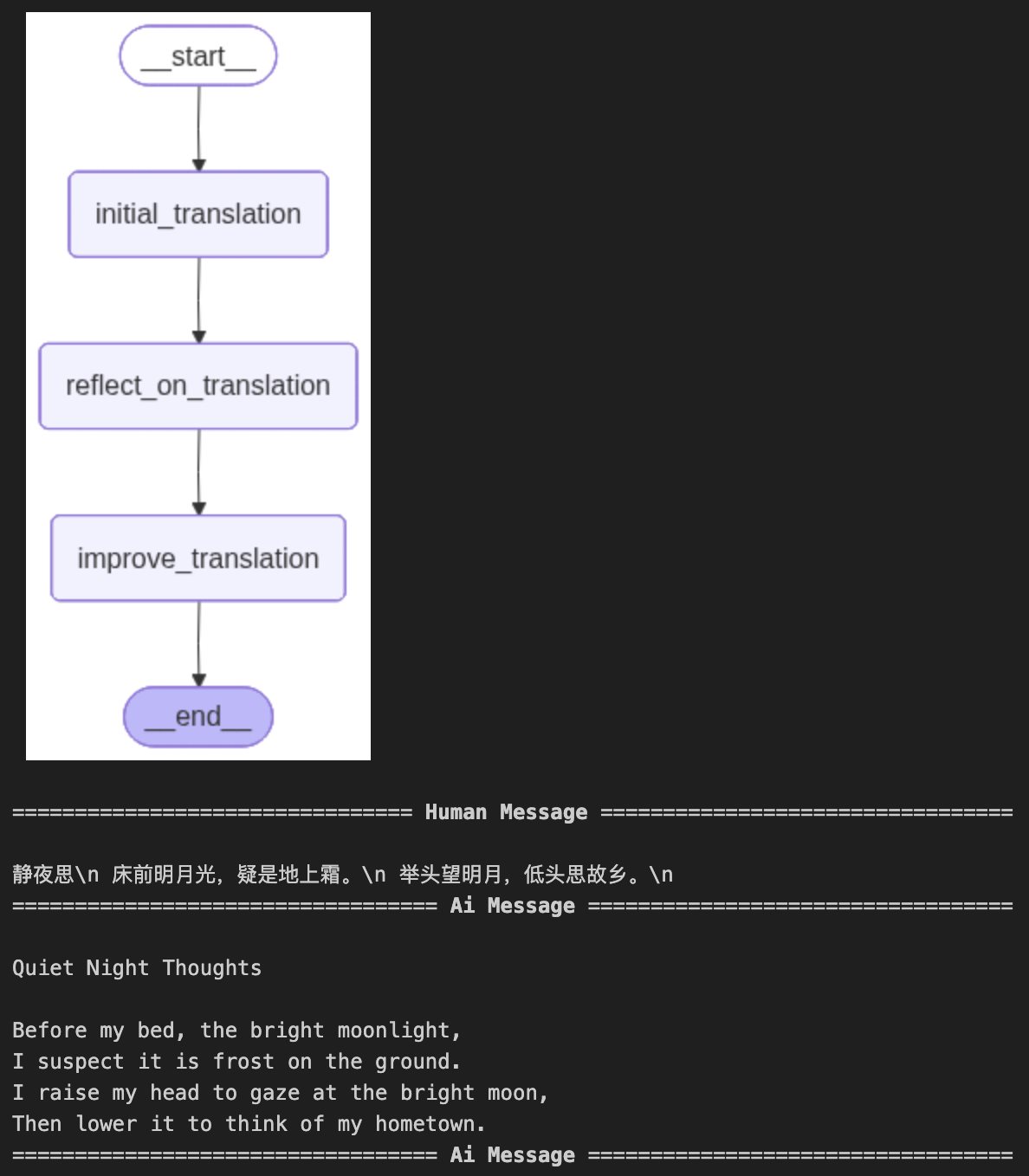
LangGraphAgent开发实战 电脑版发表于:2025/8/26 23:47  >#LangGraphAgent开发实战 [TOC] 核心概念 ------------ ### 什么是LangGraph tn2>LangGraph是一个构建在LangChain之上的库,旨在为Agent添加循环运算的能力。 我们知道LangChain主要面向定义有向无环图,一旦前面的节点失败则后面的都会失败。而LangGraph引入了循环的功能,实现了有向有环图,从而实现更复杂的Agent。<br/> LangGraph=构建Agent的框架<br/> 核心概念: 1.StatefulGraph 2.Node 3.Edges ### StatefulGraph tn2>StatefulGraph定义有向有环图及其保存的状态,需要往里面添加Node才能形成有向有环图  ### Node tn2>Node是LangGraph的节点,每个节点代表一个函数或一个计算步骤。 你可以定义节点来执行特定任务,例如处理输入、做出决策或与外部API交互。 节点相互依赖,可以是串行、并行和在某些节点循环运行  ### Edges tn2>边连接图中的节点,定义计算流程(包括起始Node和终止Node)。 LangGraph支持条件Edges,可以根据图的当前状态动态确定要执行的下一个节点。  LangGraph Chat 实践 ------------ tn2>我们这里使用单节点进行示例。 首先创建一个`langgraph_chat_example.ipynb`文件,并安装相关依赖。 ```bash ! pip install langgraph langsmith langchain-openai ``` tn2>接着用 LangGraph 搭建了一个最简单的对话工作流:定义状态保存消息 → 建立聊天节点调用大模型 → 构建并编译成对话图 → 可视化流程 → 最终实现一个命令行里的循环聊天机器人。 ```python # langgraph 简单示例 from typing import TypedDict, Annotated from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages from langgraph.graph import StateGraph from IPython.display import Image, display llm = ChatOpenAI( api_key="你的API Key" ) class State(TypedDict): messages: Annotated[list, add_messages] def chat(state: State): return {"messages": [llm.invoke(state["messages"])]} # 单节点 workflow = StateGraph(State) workflow.add_node(chat) workflow.set_entry_point("chat") #workflow.add_edge("chat", "__end__") workflow.set_finish_point("chat") graph = workflow.compile() try: display(Image(graph.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png())) except Exception: pass while True: user_input = input("User: ") if user_input.lower() in ["quit", "exit", "q"]: print("Goodbye!") break for event in graph.stream({"messages": ("user", user_input)}): for value in event.values(): print("Assistant:", value["messages"][-1].content) ```  用LangGraph实现TranslationAgent ------------ tn2>这段代码实现了一个翻译代理,我使用 LangGraph 管理翻译过程。首先,通过三个节点依次处理翻译: `initial_translation`(初步翻译), `reflect_on_translation`(反思翻译), `improve_translation`(改进翻译)。 我使用 `State` 来保存每一步的翻译历史,整个工作流按顺序执行这三个节点,确保翻译从初始到优化都能不断改进。 ```python # langgraph 实现 translation agent # langgraph 简单示例 from typing import TypedDict, Annotated from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI from langgraph.graph.message import add_messages from langgraph.graph import StateGraph from IPython.display import Image, display from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, START, END llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o", api_key="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" ) source_lang = "Chinese" target_lang = "English" class State(TypedDict): messages: Annotated[list, add_messages] def initial_translation(state: State): source_text = state["messages"][-1].content system_prompt = f"You are an expert linguist, specializing in translation from {source_lang} to {target_lang}." translation_prompt = f"""This is an {source_lang} to {target_lang} translation, please provide the {target_lang} translation for this text. \ Do not provide any explanations or text apart from the translation. {source_lang}: {source_text} {target_lang}:""" messages = [ ( "system", system_prompt, ), ("human", translation_prompt), ] return {"messages": [llm.invoke(messages)]} def reflect_on_translation(state: State): country = "America" # 获取输入的原文(User 消息) source_text = state["messages"][-2].content # 获取翻译(Assistant 消息) translation_1 = state["messages"][-1].content system_message = f"You are an expert linguist specializing in translation from {source_lang} to {target_lang}. \ You will be provided with a source text and its translation and your goal is to improve the translation." reflection_prompt = f"""Your task is to carefully read a source text and a translation from {source_lang} to {target_lang}, and then give constructive criticism and helpful suggestions to improve the translation. \ The final style and tone of the translation should match the style of {target_lang} colloquially spoken in {country}. The source text and initial translation, delimited by XML tags <SOURCE_TEXT></SOURCE_TEXT> and <TRANSLATION></TRANSLATION>, are as follows: <SOURCE_TEXT> {source_text} </SOURCE_TEXT> <TRANSLATION> {translation_1} </TRANSLATION> When writing suggestions, pay attention to whether there are ways to improve the translation's \n\ (i) accuracy (by correcting errors of addition, mistranslation, omission, or untranslated text),\n\ (ii) fluency (by applying {target_lang} grammar, spelling and punctuation rules, and ensuring there are no unnecessary repetitions),\n\ (iii) style (by ensuring the translations reflect the style of the source text and take into account any cultural context),\n\ (iv) terminology (by ensuring terminology use is consistent and reflects the source text domain; and by only ensuring you use equivalent idioms {target_lang}).\n\ Write a list of specific, helpful and constructive suggestions for improving the translation. Each suggestion should address one specific part of the translation. Output only the suggestions and nothing else.""" messages = [ ( "system", system_message, ), ("human", reflection_prompt), ] return {"messages": [llm.invoke(messages)]} def improve_translation(state: State): # 输入原文(User 消息) source_text = state["messages"][-3].content # 初始翻译结果(Assistant 消息) translation_1 = state["messages"][-2].content # 反思建议(Assistant 消息) reflection = state["messages"][-1].content system_message = f"You are an expert linguist, specializing in translation editing from {source_lang} to {target_lang}." improve_prompt = f"""Your task is to carefully read, then edit, a translation from {source_lang} to {target_lang}, taking into account a list of expert suggestions and constructive criticisms. The source text, the initial translation, and the expert linguist suggestions are delimited by XML tags <SOURCE_TEXT></SOURCE_TEXT>, <TRANSLATION></TRANSLATION> and <EXPERT_SUGGESTIONS></EXPERT_SUGGESTIONS> \ as follows: <SOURCE_TEXT> {source_text} </SOURCE_TEXT> <TRANSLATION> {translation_1} </TRANSLATION> <EXPERT_SUGGESTIONS> {reflection} </EXPERT_SUGGESTIONS> Please take into account the expert suggestions when editing the translation. Edit the translation by ensuring: (i) accuracy (by correcting errors of addition, mistranslation, omission, or untranslated text), (ii) fluency (by applying {target_lang} grammar, spelling and punctuation rules and ensuring there are no unnecessary repetitions), \ (iii) style (by ensuring the translations reflect the style of the source text) (iv) terminology (inappropriate for context, inconsistent use), or (v) other errors. Output only the new translation and nothing else.""" messages = [ ( "system", system_message, ), ("human", improve_prompt), ] return {"messages": [llm.invoke(messages)]} workflow = StateGraph(State) workflow.add_node("initial_translation", initial_translation) workflow.add_node("reflect_on_translation", reflect_on_translation) workflow.add_node("improve_translation", improve_translation) # 定义 DAG workflow.set_entry_point("initial_translation") workflow.add_edge("initial_translation", "reflect_on_translation") workflow.add_edge("reflect_on_translation", "improve_translation") workflow.add_edge("improve_translation", END) #workflow.add_edge("chat", "__end__") #workflow.set_finish_point("chat") graph = workflow.compile() try: display(Image(graph.get_graph().draw_mermaid_png())) except Exception: pass """ 静夜思\n 床前明月光,疑是地上霜。\n 举头望明月,低头思故乡。\n """ user_input = input("输入中翻英内容: ") events = graph.stream( {"messages": [("user", user_input)]}, stream_mode="values" ) for event in events: event["messages"][-1].pretty_print() # for event in graph.stream({"messages": ("user", user_input)}): # for value in event.values(): # print("Assistant:", value["messages"][-1].content) ```